“It is going help me help patients.”
Ginger Isom-Batz, MD
Certified in both Urology and Female Pelvic Medicine
Watch clinician testimonials
Diagnosing and Preventing Challenging Gynecological and Urological Infections

Female urogenital infections such as bacterial vaginosis (BV), vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are frequently recurrent and polymicrobial.
Overlapping symptoms, prior antimicrobial use, and limitations of standard culture methods often lead to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis. Chronic infections may contribute to infertility, persistent pelvic pain, and reduced quality of life.
Our Solution:
MicroGenDX provides rapid microbial DNA sequencing to improve diagnostic accuracy and clinical outcomes in women’s health. Our VaginalKEY, UroKEY, and combined WomensKEY tests are validated for vaginal swabs and urine samples to support the diagnosis and management of:
- Bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC)
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Infertility investigations and more
Powered by next-generation sequencing (NGS) and qPCR, these tests enable high-sensitivity detection of bacterial and fungal pathogens even in polymicrobial or culture-negative infections. Resistance gene profiling supports earlier, more targeted antimicrobial or antifungal therapy, helping clinicians deliver faster and more effective treatment for conditions that often present with overlapping or non-specific symptoms.
Clinical Insights from our Urine Samples
Extensive Real-World Experience:
By 2025, MicroGenDX had analyzed over 157,000 urine samples, identifying around 5,800 distinct microbial species*.
Detection Beyond Common Uropathogens:
Findings included both common pathogens (E. coli, E. faecalis) and fastidious or anaerobic bacteria often missed by culture (e.g., Atopobium vaginae, A. schaalii, Anaerococcus spp., F. magna).
More Than Just E. coli:
E. coli represented only 28% of all pathogens - 72% were other, often undetected organisms missed by conventional diagnostics.
Proven Clinical Value:
These findings highlight the diagnostic precision and clinical relevance of MicroGenDX’s NGS-based urine testing in urology
Recommended use of Next-Generation DNA Sequencing in urology and gynecology

IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America):
The IDSA recognizes the increasing utility of NGS for identifying pathogens in complex urological infections, including urinary tract infections (UTIs) and urosepsis. It is recommended for its ability to detect rare or multidrug resistant organisms that may be missed by traditional culture methods (IDSA, 2021).

ASM (American Society for Microbiology):
NGS is highlighted for its role in improving pathogen identification and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profiling in urological infections. ASM guidelines support its use in cases of recurrent infections, complicated UTIs, and infections caused by pathogens with resistant profiles (ASM, 2020).
Interpreting our lab report
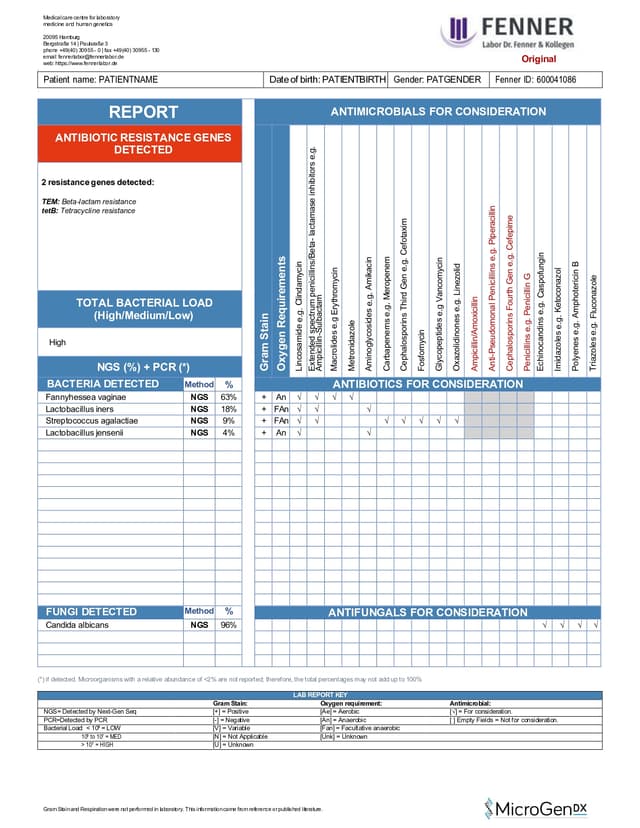
Each test includes a detailed laboratory report, providing clinicians with clear, structured data for fast decision-making.
These reports include:
• List of bacteria and fungi detected in the sample(s)
• Identified antibiotic resistance genes
• Antimicrobials to consideration for treatment


VaginalKEY-Test
Vaginal Infection Test
Vaginal Swab
NGS DNA + qPCR Diagnostics for accurate microbial identification
17 antibiotic resistance genes & list of antimicrobials for consideration
3-5 Business days (excludes transit)


WomensKEY-Test
Women`s Health Comprehensive Test
Urine, Vaginal Swab
NGS DNA + qPCR Diagnostics for accurate microbial identification
17 antibiotic resistance genes & list of antimicrobials for consideration
3-5 Business days (excludes transit)


UroKEY-Test
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Test
Urine
NGS DNA + qPCR Diagnostics for accurate microbial identification
17 antibiotic resistance genes & list of antimicrobials for consideration
3-5 Business days (excludes transit)
Publications Demonstrating the Impact of NGS in Women's Health
Significantly better pregnancy rates and live birth rate with NGS guided treatment*.
In this prospective cohort study of 195 women with recurrent implantation failure, the group where vaginal flora and endometrial microbiota were analyzed by microbial 16S rRNA gene sequencing and subsequently treated with antibiotics followed by probiotics according to the pathogens detected achieved cumulative clinical pregnancy 64.5% and ongoing pregnancy rate 48.9% after two frozen embryo transfers, while the control group showed 33.3% and 31.2% respectively.
By examining the uterine microbiota and administering targeted antibiotics, broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment was avoided, and the percentage of endometrial Lactobacillus spp. improved from 25.8% to 90.8%.
 *Iwami N et al., Therapeutic intervention based on gene sequencing analysis of microbial 16S ribosomal RNA of the intra-uterine microbiome improves pregnancy outcomes in IVF patients: a prospective cohort study . Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. 2023.
*Iwami N et al., Therapeutic intervention based on gene sequencing analysis of microbial 16S ribosomal RNA of the intra-uterine microbiome improves pregnancy outcomes in IVF patients: a prospective cohort study . Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. 2023.Urine NGS can significantly increase the diagnostic sensitivity compared to traditional urine culture methods, especially in RC patients
Better sensitivity: In women with recurrent bladder infections, next-generation sequencing (NGS) identified bacteria in 67.7% of cases, while standard urine cultures detected bacteria in only 16,7% of cases.
NGS revealed a broader range of bacteria, including species like Sphingomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Rothia, and others were further identified by urine NGS , which were not detected by traditional urine cultures.
 Urinary Microbiome Characteristics in Female Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Recurrent Cystitis
Urinary Microbiome Characteristics in Female Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Recurrent CystitisSignificantly better outcomes for UTIs with NGS guided antibiotic selection
Better sensitivity: by NGS: In symptomatic UTI patients 13 of 44 had positive urine culture whereas 44 of 44 patients had positive DNA NGS results.
Treatment decisions guided by NGS results led to significantly better patient outcomes, with symptom scores more than doubling compared to those treated based on culture (8.5 vs. 3.7; p < 0.001). Head-to-head comparison study.
 McDonald W. M., Kameh D., Johnson E. M.,. et al. A Head-to-head Comparative Phase II Study of Standard Urine Culture and Sensitivity vs DNA NGS Testing for UTI. Reviews in Urology, 2017
McDonald W. M., Kameh D., Johnson E. M.,. et al. A Head-to-head Comparative Phase II Study of Standard Urine Culture and Sensitivity vs DNA NGS Testing for UTI. Reviews in Urology, 2017Clinical cases where MicroGenDX test helped achieve treatment success
Patient with urinary tract infection
An 82-year-old woman with a history of recurrent UTI, and who had been treated for E. coli, presented to the clinic with an acute episode. A mid-stream urine sample was obtained and sent for standard urinalysis, C&S, PCR by Volente Laboratories and MD Labs, and NGS by MicroGenDX.
There was a high concordance between C&S and PCR-based techniques to detect a high load of E. coli (>105 per ml). All testing identified E. coli, but NGS was the only lab that detected the dominant pathogen as Bacteroides fragilis (50%). Based on the anaerobic B. frag and quinolone-resistant genes detected by NGS, the patient was switched to a targeted antimicrobial therapy using clindamycin for a total of 14 days. By the fifth day, the patient’s symptoms subsided, and upon follow-up on day 14, she had no symptoms.
Inquire about our test
Send us a message using the form below, or email us at info@microgendx.eu
